This modern life delivers a “gut punch” of health issues…
High stress levels, too little sleep, eating ultra-processed and high-sugar foods, can all damage our gut microbiome.
The result: complications with our health, from unintentional weight changes, fatigue, skin irritation, autoimmune conditions, and food intolerances.
Let’s change that, because your gut microbiome is the key to a healthy digestive system, synthesizing important nutrients, and regulating your immune system.
But make no mistake, imbalances in your gut microbiome can cause a whole host of health problems, including obesity, diabetes, and even neurological disorders like Parkinson’s disease and depression.
What are Probiotics & Prebiotics?
Probiotics are “live microorganisms, which when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host.”
Put simply: Probiotics are good bacteria (and sometimes yeasts) that offer health benefits.
So how do probiotics work?
The main job of probiotics, or good bacteria, is to maintain a healthy balance in your body.
When you are sick, bad bacteria invades your body and increases in number. This makes you feel out of balance or sick. Now the good bacteria work hard to fight off the bad bacteria to bring back the balance within your body and make you feel better again – Well done probiotics!
Prebiotics are special plant fibers that help the healthy bacteria grow in your gut. This makes your digestive system work better.
You can say that prebiotics are the food source for probiotics.
Prebiotics are found in carbohydrates that your body can’t digest. So they go to your lower digestive tract, where they then act like food to help the healthy bacteria grow.
Bottom line: Without prebiotics there’s no food for the probiotics.
That means the probiotics can’t do their job effectively, which leads to problems in your gut microbiota.
The Benefits
We can see how probiotics and prebiotics can provide your body with powerful benefits from an overhead view.
The current studies show that probiotics may improve digestive health, mental health like reducing depression for example, gastrointestinal health and heart health. Plus, evidence suggests they may even give you healthier-looking skin.
Prebiotics, similarly, have many links to the benefits of probiotics.
They may support a healthy gut, offer better digestive health, and help to lower antibiotic-related health problems. They may also improve your body’s absorption of calcium and can help process foods faster, so they spend less time in your digestive system, which helps avoid constipation.
Foods To Keep Your Gut Microbiota Healthy Via Prebiotics
For Prebiotics: Eat lots of vegetables, fruits, beans and legumes
Both fruits, vegetables, beans and legumes are great sources of nutrients for a healthy microbiome. They are high in fiber, which your gut loves. Here are some specific foods high in fiber that are great for your gut bacteria, and should be on your shopping list:
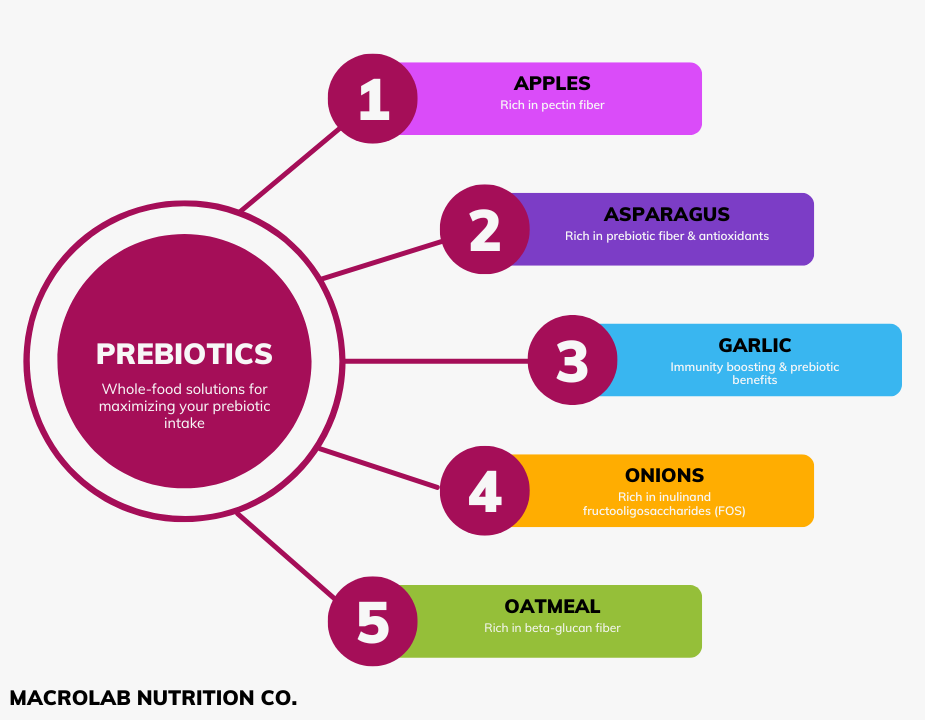
Foods To Keep Your Gut Microbiota Healthy Via Prebiotics
Probiotic: Eat fermented foods
Fermented foods have undergone a process in which the sugars they contain are broken down by yeast or bacteria. Fermented foods are packed with probiotics and may therefore improve your gut health.
Here’s 5 fermented foods to add to your shopping list:
- Yogurt – Yogurt is a great sources of probiotics.
- It is made from milk that has been fermented by friendly bacteria, mainly lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria. Plant-based yogurts, such as coconut yogurt, also contain added friendly bacteria.
- Unfortunately, not all yogurt contains live probiotics because they have been killed during processing. Therefore, look for yogurt with active or live cultures.
- Kimchi – Kimchi is a fermented, spicy Korean side dish usually with cabbage as main ingredient, but it can also be made from other vegetables. K
- Kimchi contains the lactic acid bacteria lactobacillus kimchi and is also high in vitamin K, vitamin B2 and iron.
- Sauerkraut – Sauerkraut is finely shredded cabbage that has been fermented by lactic acid bacteria. It is a traditional and old food very popular particularly in Europe.
- In addition to its probiotic qualities, sauerkraut is rich in fiber, the minerals iron and manganese and the vitamins C, B and K.
- Make sure to choose unpasteurized sauerkraut, because pasteurization kills the live and active bacteria.
- In addition to its probiotic qualities, sauerkraut is rich in fiber, the minerals iron and manganese and the vitamins C, B and K.
- Kefir – Kefir is a fermented probiotic milk drink. It is made by adding kefir grains to milk from cows or goats. Kefir grains are cultures of lactic acid bacteria and yeast that look a bit like a cauliflower.
- Tempeh – Tempeh is fermented soybean. It is normally served as a popular, high protein substitute for meat.
- Due to fermentation tempeh also contains vitamin B12. This makes it a great choice for vegetarians as well as anyone looking to add a nutritious probiotic to their diet.
The Outcome
The best way to maintain a healthy gut microbiota is to eat a varied diet with a range of fresh, whole foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes and fermented foods as we know, but applying that to everyday practice can be difficult unless you’re regularly consuming these foods.
Try these bonus tips below to up your intake:
Bonus tips:
- Try trading milk for kefir or yogurt in a smoothie!
- Add tempeh to your favorite stir-fry recipes!
- Serve sauerkraut as a side dish or try adding it in a soup!
- Experiment with kimchi. Add it to your rice or make delicious fritters or pancakes out of it!
Cheers,
Coach Beau

